Innovations in component technology address latest requirements of 5G mobile equipment designs
Read this to find out about:
• Why new types of 5G equipment require components which are more robust and smaller, and offer higher signal integrity
• New resistor designs for 5G applications which are resistant to solder joint cracking under temperature stress
• The latest miniature relays for densely populated power distribution units
The steady advance of mobile networking technology has delivered many benefits to consumers. In the 21st century, the move from 2G through 3G to 4G came in tandem with the transformation of the mobile phone from a simple device for voice calling to a high-specification mobile computer providing broadband internet access.
Now the next stage in mobile evolution, 5G, is rolling out worldwide, bringing a new set of capabilities: in particular, 5G is the first mobile networking technology to truly meet the needs of the mobile Internet of Things (IoT). In addition, 5G technology provides for much denser concentrations of networked devices in a cell, and supports much lower-latency and high-bandwidth communication. This means that new types of mobile network infrastructure have emerged:
- New ‘small cell’ micro-base stations allow for lower-cost installations in city centers to support the connection of huge numbers of IoT devices
- 5G customer premises equipment (CPE) installed in homes and offices provides a wireless broadband internet access point, an alternative to traditional wired copper or optical internet connections to the end user
- Ever larger data centers supporting the mobile network provide higher capacity to handle the greatly increased volumes of data traffic that the 5G air interface can support
The changing nature of mobile network infrastructure is placing new demands on equipment manufacturers, and this is in turn driving the development of new and improved electronics components for 5G equipment. The most important of these demands are:
- Increased robustness to cope with higher-power electrical connections and harsh exterior conditions, including high temperatures, and airborne contaminants such as atmospheric sulfur
- Miniaturization, where tight space constraints strongly affect the component choices made by the designers of small cells intended for installation in the city center, of CPE gateways mounted on the outside wall of a consumer’s home, and of data centers
- Higher signal integrity, which is required to maintain high data quality and minimize bit errors in 5G networks which operate at higher frequency and higher data rates than previous mobile network technologies
These new requirements are determining the component selection decisions made by manufacturers of 5G network modules and systems, and in response Panasonic has developed new products and technologies in important component categories such as resistors, capacitors, connectors, and relays. This article describes how these new components are rising to the challenge of 5G.
Robust components handle harsh operating conditions
Whether mounted on a traditional tall mast or affixed to the wall of a city center building, a 5G antenna, remote radio head (RRH) or baseband unit (BBU) is exposed to extremes of temperature and to atmospheric sulfur. These are conditions in which standard commercial components, intended for use indoors, are at risk of premature failure.
The specifications for the precision resistors used in 5G equipment require particularly careful attention. The temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) shows the drift in resistance as the operating temperature changes, while the maximum operating temperature and temperature derating threshold indicate the upper limits of the resistor’s temperature capabilities.
These capabilities are being stretched because miniaturization means that heat-dissipating components are packed more closely together with less space for cooling airflows. In response, Panasonic has created the new ERJ-H family of thick-film precision resistors which offer superior temperature characteristics. The ERJ-H resistors meet the need in two ways:
- The maximum operating temperature has been lifted in the ERJ-H from 155°C to 175°C compared to the existing ERJ resistors, and the temperature derating threshold from 70°C to 105°C, shown in Figure 1
- The resistors have been miniaturized, for instance the ERJHP6 offers an equivalent resistance value and power rating in the 0805 case size to the ERJP14 in a 1210 case, a two-step reduction in case size. The smaller the case size, the less mechanical stress is applied to solder joints by thermal shrinkage and expansion. This means that the ERJ-H series resistors pose a smaller risk of solder joint cracking than the ERJ resistors when operating in 5G equipment
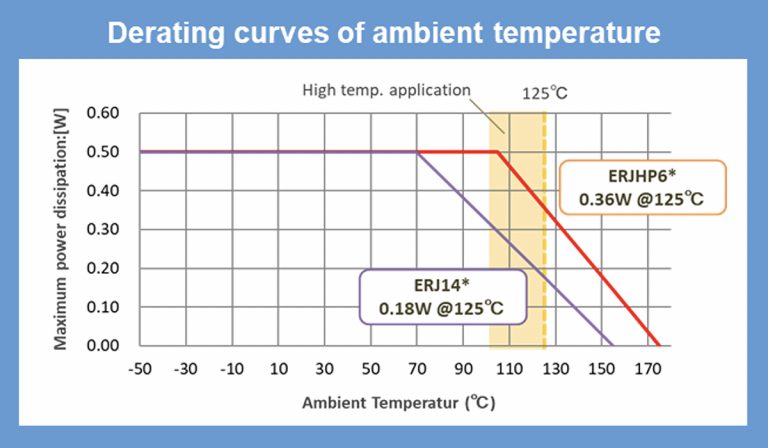
Fig. 1: Derating curves of the ERJ-H high-temperature family compared to the ERJ resistors
Mobile network operators’ business model for 5G systems requires reliable operation and minimal unplanned downtime. Both thermal stress and sulfur contamination can cause component failure. Panasonic addresses the need for high sulfur resistance while providing designers with a choice of features and benefits.
The ERJ-S thick-film resistors have gold inner electrodes, and gold is inherently immune to sulfur corrosion.
The ERJ-U thick-film resistors have silver-palladium alloy inner electrodes which are highly resistant to sulfur corrosion, and which also survive 12,000 hours of immersion in an oil bath
The ERA-V series of thin-film resistors has a new structure which helps to protect the inner electrode, enhancing sulfur resistance, and which absorbs stress to reduce the risk of solder joint cracking, as shown in Figure 2. The ERA-V series resistors also feature a new, smoother substrate which reduces localized current density. As a result, the ERA-V resistors now offer a much higher ESD rating than the earlier ERA-A series, up to 2 kV, with only small changes in resistance when exposed to even higher ESD strikes up to 4 kV.
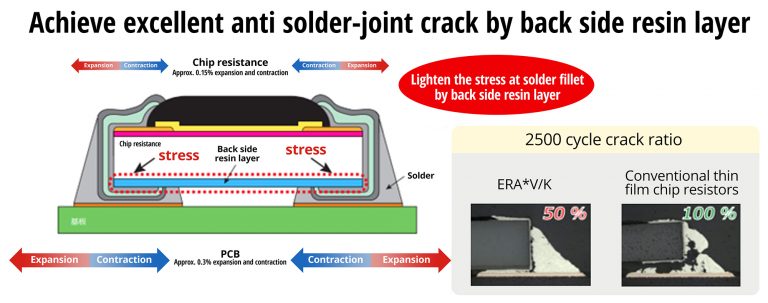
Fig. 2: The new structure of the ERA-V resistor features a stress absorbing layer
Panasonic’s efforts to offer more robust components to designers of 5G equipment extend beyond its families of resistors to include its portfolio of electromechanical relays. In data centers, automatic transfer switch applications support hot-swappable redundant power supplies. In the event of a power failure, a relay is required to perform high-current switching in the transition from the main power supply to the redundant power supply. To meet this requirement, Panasonic supplies the HE-S relay family, which carries two channels of 35 A, and which provides an auxiliary contact to detect contact welding. Very low coil holding power helps to reduce system power consumption.
Design options are widened further by the HE-PV family of relays, which offer 48 A and 90 A current ratings.
Space-saving components support system miniaturization
New relay technology is also coming to the support of 5G equipment manufacturers’ miniaturization efforts, as well as providing more robust component options. Space-saving relays are of particular interest to manufacturers of the power distribution units (PDUs) which supply arrays of servers in 5G network data centers. These rack-mounted PDUs have very tight space constraints, and can feature as many as 48 relays on a single unit.
The DW family of PCB single-pole single-throw (SPST) relays with latching capability is ideal for this application because of the very small board footprint, giving the PDU designer greater flexibility in board layout, and promoting improved airflow and thermal dissipation from high-power components, shown in Figure 3. The latching feature also ensures the switch timing is consistent, making it easier to implement a more effective zero-cross circuit to prolong the life of the relay. The high inrush type DW series has a current switching rating of 16 A at 277 V ac, but has an option to switch up to 20 A to accommodate the higher-power PDU designs required by market segments such as cryptocurrency mining.
The DW relays are also offered with a double-pin option in the same SPST configuration. The extra pins allow for better heat dissipation from the contacts, which generate most of the heat inside a relay. This double-pin option also increases the relay’s short-circuit rating, a crucial characteristic in PDUs. A PDU is a high-cost item. One of the most obvious failure modes of a PDU is a short-circuit generated when the PDU is inserted wrongly into a system through human error. The DW relays’ high short-circuit withstanding capability protects the board against the risk of damage, helping to save the operator from potentially large equipment replacement costs.

Fig. 3: The DW relay has a small board footprint and a high current capability
In a different product category, the miniaturization trend in 5G equipment is equally at work. Panasonic supplies a broad choice of POSCAP™ tantalum-polymer and SP-CAP™ polymer aluminium capacitors. These low-profile capacitors are notable for high temperature capability and long lifetime as well as small size.
Providing confidence in the performance and quality of the space-saving Panasonic capacitors, both POSCAP and SP-CAP family devices are specified in 5G networking equipment reference design boards developed by many of the world’s leading suppliers of microprocessors and FPGAs.
High signal integrity supports reliable mobile broadband connectivity
The third of the three trends driving component selection for 5G mobile network equipment is signal integrity, to maintain reliable communications at the very high frequencies and data-transfer rates at which 5G base stations and terminals operate.
This is why Panasonic has developed a family of RF connectors which are optimized for the 5G millimeter-wave frequencies. At these frequencies, signals are highly sensitive to electro-magnetic interference (EMI) generated by components close to the connector on densely populated circuit boards. This means that RF connectors require highly effective shielding to screen out the interfering frequencies.
The Panasonic 5G RF connectors benefit from a unique construction which provides for class-leading signal integrity and robustness, and in addition, offer a footprint some 16% smaller than that of directly competing devices, to aid miniaturization.
The unique features of the Panasonic 5G connectors include:
- Insert molding with metal shield. This construction, which requires advanced production equipment and techniques to be manufactured in volume, isolates the pins which carry high-frequency signals, insulating them from EMI and dramatically improving signal integrity.
- Tough Contact pins. In competing connectors, pins are typically manufactured with a stamping process. In the Panasonic 5G RF connectors, the pins are bent and rolled, a process implemented with special tooling, which makes the pins stronger and more flexible, so that the connector is better able to withstand shock and vibration. This contributes to signal integrity by maintaining a secure physical connection under all operating conditions.
Continuous improvement of products for next-generation communications
This article has highlighted the product developments which enable 5G mobile equipment manufacturers to compete successfully in a market which demands more robustness, continued miniaturization and high signal integrity.
Innovation at Panasonic never stops, however. In the world of broadband connectivity and mobile infrastructure, the most eye-catching of the product developments on the horizon is a family of DC switching relays, for use in new all-dc power architectures for data centers, which will avoid the losses incurred when converting mains ac to a dc supply to servers.
The design of a DC switching relay is extremely challenging: whereas an ac relay can switch at 0 V to avoid arcing, a DC switching relay always switches under load, which creates substantially more arcing than in an AC relay.
Panasonic is now developing a new family of DC switching relays which will use novel methods to manage safely the dissipation of arcing energy, and to enhance the design of the relay’s contacts to counteract the pitting and material deposition caused by switching under load.
This, and many other innovations in resistor, capacitor and connector design, will ensure that Panasonic components continue to meet the new and emerging demands of manufacturers serving the 5G equipment market.
